“Information is the oxygen of the digital era, now it's your choice to pollute with cyber threats or purify with SIEM solutions”
Security Information and Event Management
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) offers a comprehensive view of an organization’s information security by centralizing the security notifications from various end point security devices. SIEM combines two security solutions, Security Information Management (SIM) and Security Event Management (SEM) into one enterprise solution.
SIEM solutions turns security events into actionable items using predefined rules and statistical correlations. It helps security and IT teams to detect and manage threats in real time.
Security Information Management (SIM) retrieves data from log files for incident analysis and reports on security threats and events.
Security Event Management (SEM) performs real time threat monitoring, correlating security events and addressing security events.
SIEM consolidate, parse and analyse the log files collected from disparate sources of network and enables Artificial Intelligence (AI) program in SIEM solutions to correlate the security events and hunt for potential threats. If an event triggers a SIEM rule, the system notifies IT teams to enact a solution.
Evolving SIEM Workflow for Advanced Threat Detection
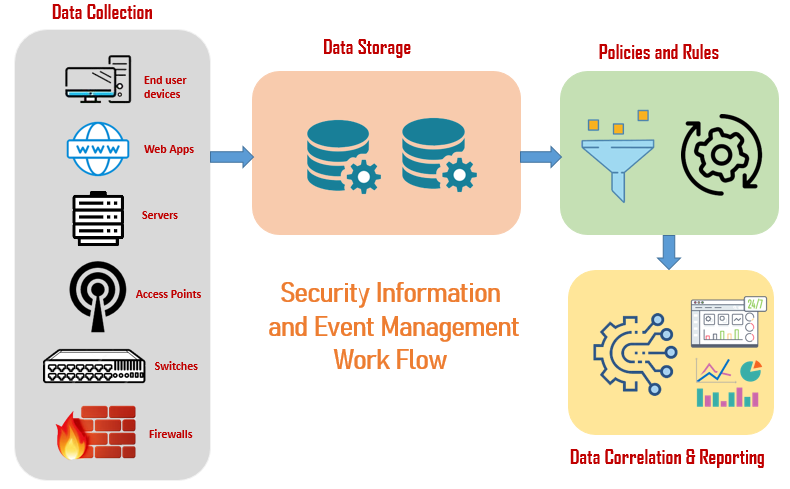
Data Collection
SIEM system collects and aggregates enormous amount of log data in the network by deploying collection agents on end user devices, workstations, servers, network devices like switches, routers and security systems like antivirus, IDS/IPS, firewalls etc. Modern SIEM solutions can obtain the log data of cloud applications by deploying edge collectors onto the cloud infrastructure.
Edge collectors also perform normalization and aggregation on log data collected from the network of an organization.
Data Storage
Traditional SIEM solutions used to rely on storage systems deployed in the data centre that created troubles to store and manage large volumes of data. Next-generation SIEM systems are built on modern technology such as Amazon S3 or Hadoop permitting unlimited storage with scalability at low cost and allows to retain and analyse log data from discrete sources of platforms and systems.
Policies and Rules
The SIEM allows security staff to define policies and thresholds that helps to aggregate logs and categorize security events such as successful and failed logons, exploit attempts, malware activity, and port scans. Moreover SIEMs leverage threat intelligence and machine learning to define rules on the data and escorts security events that require further investigation.
Data Correlation and Reporting
The main objective of a SIEM solution is to centralize log data and consolidate it by correlating logs and events into meaningful security incidents.
Multiple events are combined and correlated to identifiable patterns that threatens security and imposes alerts on successful match. Event correlation encompass Data Intelligence, Root Cause Analysis, Fraud Detection and Operations Support use cases to report accurate security incidents.
SIEM Components and Capabilities
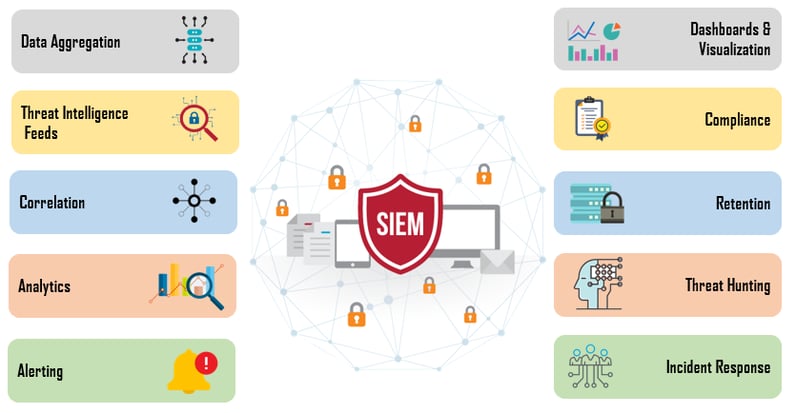 Data Aggregation
Data Aggregation
Aggregates log data from various end user devices, servers, databases, network devices like switches, routers and security devices like antivirus, firewalls and IDS/IPS.
Threat Intelligence Feeds
Threat intelligence containing pre-defined vulnerable data, threat actors and attack patterns is applied to collected log data.
Correlation
Links events and multiple data points into meaningful security incident, threat or forensic finding.
Analytics
Leverages machine learning algorithms and statistical features to identify deeper relationships between security events and compared to known threat patterns.
Alerting
Trigger alerts and notifies security team via emails, messages or security dashboards on successful match of events to identifiable patterns.
Dashboards and Visualizations
Visualizing security events via dashboards allows security staff to review event data and corresponding patterns.
Compliance
Generate reports that adapts global security standards like HIPPA, PCI/DSS, GDPR etc. for the purpose of compliance and auditing processes.
Retention
Retains historical data that enable forensic investigations for zero day attacks and mislaid threats.
Threat Hunting
Enables security team to execute queries on SIEM data and filters to proactively uncover potential threats or breaches.
Incident Response
Provides case management and applicable solutions to security incidents that enable security staff to quickly synchronize the essential data and respond to a threat.
SIEM Leverages over Potential Threats
SIEM permits IT team to spot, analyse and respond to potential security threats quicker through its centralized log collection and even correlation features. Implementing SIEM solutions into organizations network acquires good deal of advantages as mentioned below:
- Preventing potential security threats
- Reducing the impact of security breaches
- Cost reduction
- Better reporting and efficient log analysis
- IT compliance
SIEM Setup and Delivery Model
Organizations follow a sequence of steps while integrating SIEM solutions to tackle advanced security threats that imposes significant impact on organizations security.
1. Guidance and Planning
This phase engages to communicate the business and technical objectives that govern the design and use of SIEM.
2. Infrastructure
Designing and implementation of servers, software’s, log collectors, and appliances comprising the SIEM system architecture.
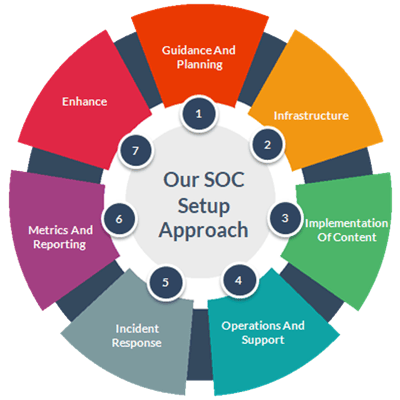 3. Implementation of Content
3. Implementation of Content
Designing, integration and implementation of all components needed to generate required alerts and visibility (feeds, rules, filters, dashboards, reports, alerts).
4. Operations and Support
Defining and managing the processes that ensures ongoing management and tuning of SIEM for continuous improvement.
5. Incident Response
Defining key principles and responsibilities for workflows to ensure streamlined incident identification, evolution and remediation at the earliest.
6. Metrics and Reporting
Evaluate the SIEM tool metrics like number of events collected and processed per second - Events per Second (EPS), log source count and alerts triggered count. Operational metrics like alerts handled/analyst/rule/target and alert response timing etc.
7. Enhance
Continuously improve and enhance the solution capabilities based on new requirements and gain operational efficiencies for the people, processes and tools involved.
How Do I Select Right SIEM Tool for My Business
Implementing SIEM builds strong security posture and improves collaboration between IT and security teams. In this competitive world multiple SIEM vendors are working hard to enhance their products to bring advanced threat detection, forensics and incident management as enterprise security solution.
Every SIEM tool has its own strategies and features to achieve SIEM workflow. Selecting appropriate tool depends on individual organization business requirements and budget.
Splunk
Splunk provides enhanced security operations like distinct log analysis, statistical analysis, AI based classification, alert management and customizable dashboards.
Splunk is available in three editions:
1) Splunk Enterprise: It is used for large IT business to collect and analyse data from distinct applications
2) Splunk Cloud: It works same as enterprise for cloud platforms
3) Splunk Light: It is a free version that collect and analyse logs, but with limited features.
Features
- Splunk enhances GUI by generating graphs, alerts and dashboards for real time data
- Creates centralized repository for data collection from various sources
- Event sequencing allows to search and investigate incidents quicker
- Automated workflows for quick and accurate response
- Supports Windows, Linux, Mac and Solaris
McAfee ESM
McAfee ESM visualizes real time activities of various servers, databases, applications and network devices of an organization.
It utilizes security products like advanced correlation engine, event receiver, event manager & investigator, and global threat intelligence to generate actionable data from McAfee ESM.
Features
- Prioritizes alerts and generates actionable data to respond and investigate quicker
- Evaluates system security by running through active directory records
- Capable to collect and analyse data from heterogeneous sources
- Supports Windows and Mac OS
Conclusion
In digital encyclopaedia, there is a tremendous growth in cybercrimes subject to internal and external threats. Implementing SIEM solution requires highly skilled security expertise to analyse and respond to the alerts triggered by the AI integrated SIEM tools. Also, it is important to understand potential threat patterns and importing it to the tool for automated detection of advanced threats.
Author Bio: Silpa is a Senior Security Analyst with Innominds and is a part of Enterprise Security Services (ESS) group. She has more than 6 years of expertise in information security with specialization in application security, network security assessments and SIEM solutions. Silpa is involved in executing and delivering the security solutions to our enterprise and ISV costumers.
Silpa is a Career Hacker, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) and Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP),