In the past few years, IT has witnessed an evolution of virtualization in the form of cloud computing and as a model that views everything “As a Service”. With the use of virtualization, the idea of sharing computing resources across multiple operating systems to increase scalability, reduce costs and enable easy administration of IT infrastructure, has become a reality. Cloud-based testing can accelerate application development and help enterprises meet their Digital Next goals.

The cloud-based environment for software testing enables testing in various environments. Projects that require large infrastructure with a limited test budget and have strict deadlines, cost management focus, with little or no reuse of tests can leverage cloud testing.
The presence of global users, the need for high quality service delivery and avoiding outages are some of the other challenges that imply the need for testing outside the datacentre. Cloud-based testing is the practical solution to all these problems. Cloud-based testing also provides effective unlimited storage, flexibility and availability of distributed testing environment, quick availability of the infrastructure with scalability, reducing the execution time of testing of large applications and thereby, costs.
Additionally, the effective usage of virtualized resources and shared cloud infrastructure results in removing redundant computer resources and software licensing costs in a test laboratory. Cloud-based testing reduces the testing setup time from weeks to minutes. A QA organization can easily leverage scalable cloud system infrastructure to check and evaluate the system.
Features of Cloud-based Testing
-
Supports a variety of end-to-end testing
Combines the power of functional test automation, API/Web service testing, performance testing and security testing. -
Integrates with Continuous Delivery tools
Facilitates Continuous Integration (Jenkins, TFS etc.)
Integrates to SOAP UI, JMeter, OWASP, ZAP
Helps execute mobile web automation scripts across multiple devices -
Integrates with Cloud services
Integrates with Cloud services like Sauce Labs for Web, mobile testing and parallel cross browser testing with no additional scripting.
Reduces test automation effort by 20% through pre-defined generic test scripts.
Cloud Testing Environments
There are three types of Cloud testing environments where the quality of applications deployed needs to be validated. Performing software testing in the cloud means accessing the flexible self-service infrastructure that is hosted off premises (public cloud), behind the corporate firewall (dedicated or private cloud) and in a hybrid cloud.
What to look out for in Cloud-based Testing
- Interaction between the components: Cloud-based testing can get challenging when there has to be an interaction between the components because the tester will have to anticipate risks like crashes, network and breakdown.
- Integration testing: Testers can lack control over the underlying environment in integration testing while testing the network, database, servers, etc.
- Interoperability with public cloud providers: Presently, there are no universal/standard solutions to integrate public cloud resources with user companies’ internal datacentre resources. Public cloud providers have their own architecture, operating models and pricing mechanisms and offer little or no inter-operability. This poses an enormous challenge for companies once they switch vendors.
- Performance of an application in private clouds: It will be shared across many users and hence could lead to delays. Also, just in case of some maintenance or outage related activities, the bandwidth could be insufficient.
- Data integrity: Cloud storage moves the user’s data to large datacentres which are remotely located and on which the user does not have any control. This unique feature of the cloud poses many new security challenges which require to be clearly understood and resolved. As the data is physically not accessible to the user, the cloud should enable the user to see if the integrity of the data is maintained or is compromised.
- Availability: The cloud-based service/environment/application should be available all the time, especially the business-critical ones. Service unavailability impacts service assurance.
- Acceptability: This determines whether an organisation is ready to use a cloud-based environment owing to security and other reasons. What surety does an existing business rely on that their third-party solution is suitable for its intended use? An organisation can easily leverage scalable cloud infrastructure to test and evaluate system (SaaS/ Cloud/ Application) performance and scalability.
Delivery Models for Cloud
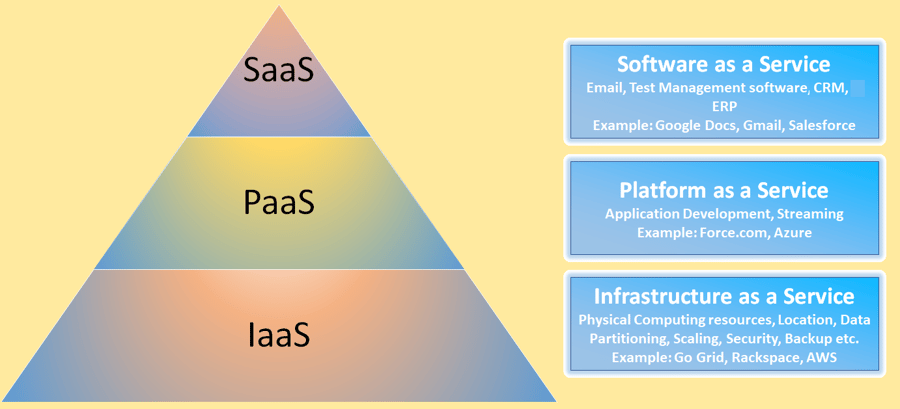
The cloud has mainly three delivery models that provide "as a Service" capabilities.
- Software as a Service (SaaS)[Consume]: The topmost layer is the application layer which is visible to the end user. Here, the applications are available to the users on demand via the internet. Hence, instead of acquiring licenses for a particular user, it proves to be the most cost-effective way of making sure that the license is always in use. Examples are Gmail, Google docs etc.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)[Build]: The central layer in the cloud is the platform layer. In this, there is no control over the underlying infrastructure, but deployed applications can be used. Hence, this provides the entire environment on demand which could be a staging or test environment. Therefore, in this model, the resource is a VM that contains the complete environment like OS, browsers, and other middleware etc. and available when it is required by a user.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)[Migrate]: This is a fundamental layer which forms the building block of the cloud. It mainly comprises physical devices such as storage, network devices, other servers etc. All these resources are available on demand, where a user pays as per the cloud service usage.
Types of Testing Performed in the Cloud
- Automation Testing – The users need to make sure that the automation suites are created and executed with minimal changes within the cloud.
- Performance Testing - Verify the network latency and reaction time, load balancing, peak request count by hosting subscription in several data centres across the world. Adding to those, traditional load and stress testing are required to validate business scenarios within the cloud model in terms of varying dynamic load and stress on the application under test.
- Availability Testing - Cloud offering should be available 24*7 for the enterprise or a user.
- Scalability Testing - Cloud providers offer options to increase or decrease the required cloud configurations as per requirement. Most cloud services have options to choose licenses on a month-on-month basis.
- Accessibility Testing - Verify user groups across different geographic locations are accessible to the cloud at any point of time without any problem.
- System integration testing (SIT) – This is performed to verify that the cloud solution will work within this infrastructure and environments, proving that the integration of multiple application modules can be easily and efficiently tested.
- User acceptance Testing (UAT) - Testing is done to verify the present provided cloud solution from the vendor meets the business needs of an organization.
- Interoperability Testing - Migration from one cloud to alternate cloud provider should have the required flexibility. Technically, it should not be a problem if a business/user is migrating from one cloud infrastructure to another one.
- Disaster Recovery Testing - Recovery option available in case a system crashes under high load/volume of data, hardware failures, system failures, Network outage, insufficient bandwidth) as per SLA. Also, it needs to be verified that if there is any data loss during this process and the amount of time it takes to report failure.
- Security Testing - All sensitive and important information which are going to be stored in the cloud will be highly secure in nature. As privacy is also a key area in cloud from the user point of view, it is important to verify the privacy of the application users and associated information when maintained in the cloud.
Conclusion
Using cloud for testing is helping organizations to speed up testing, acquire software licenses and provide infrastructure at a significantly lower cost without having to set it up and later worry about capacity utilization.
Evidently, the cloud is a requirement and cloud-based testing is desirable for every test organisation to meet technological challenges and save precious time.