Fifty-seven percent of mobility decision makers surveyed in the Forrester Analytics Global Business Technographics® Mobility Survey, 2019, said that they have edge computing on their roadmap for the next 12 months, which is significant when considering how recently edge computing arrived in the sphere of technology evolution.
Overview
Edge Computing is a buzz phrase in the ascendance and a hot topic, too. According to a report by Gartner, by the year 2022, around 75% of enterprise-generated data would be processed outside the traditional, centralised data centre or cloud. Before we move ahead with the nitty-gritty of edge computing, let’s decipher what exactly is edge computing. To put it simply, it is an extension of core cloud computing. Going by this definition, edge computing, essentially, becomes more important and fundamental in nature. There aren’t any straight answers for this question. For some, it is the distinction between data processed centrally to provide information, and data processed at the periphery to trigger action, as is the case with automated systems and IoT. On the other side of the spectrum are people for whom, it is just another form of cloud computing.
Importance of Edge Computing
The biggest benefits organisations seek from edge computing include flexibility to handle present and future artificial intelligence demands and the fact that computing at the edge avoids network latency and allows faster responses. Edge computing allows data generated by IoT devices to be processed closer to its source instead of sending it across storage networks. This, in turn, helps organisations to analyse the data in real-time.
At the hindsight, edge computing isn’t a new phenomenon as it has already been used for 4G. One of the most important aspect of edge computing is the massive rise of Machine-Type Communications (MTC), most notably, the Internet of Things (IoT). With regards to 5G, it is easily scalable to accommodate hundreds of IoT devices and the traffic resulting from it would overload core networks. This process can be halted if and when majority of data is pre-processed at the edge and only essential signals are sent back to headquarters.

According to the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC), every connected device requires some sort of compute capability at the edge. However, the immense power of edge computing isn’t being utilised and organisations aren’t cognizant of its capabilities when it comes to solving industrial internet users’ challenges.
Role of Edge Computing
The first and foremost role of edge computing is to store and send data to the cloud systems. Edge computing comes handy as it reduces the latency because the data isn’t required to travel through a network to a central data center. This works miracles for manufacturing and financial services. Even though, IoT is in the driver’s seat when it comes to edge computing, other technologies are doing their part in increasing the pace of adoption of edge computing ecosystem.
The use of this technology beyond the realms of mobiles and desktops has given rise to Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC). This kind of computing allows various types of access at the edge. Essentially, MEC is a network architecture that brings access to radio network information that assists operators to expose and open their networks to a new ecosystem.
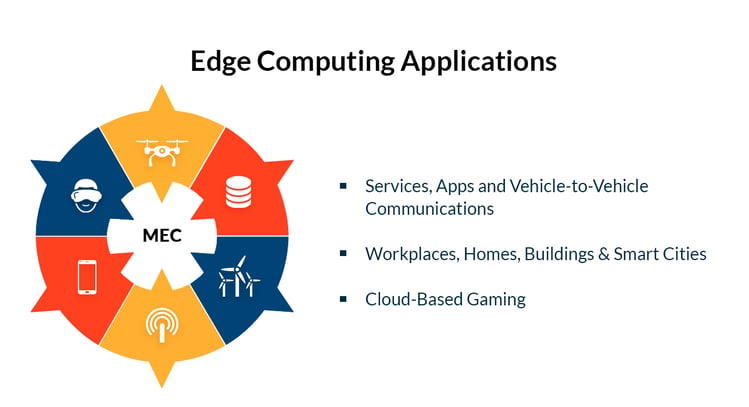
Advantages of Using Edge Computing
By the year 2025, IIoT will create USD7.5 Trillion in value. This essentially means that connected devices will generate a huge volume of data, even though cloud will continue to play an important role in enabling new levels of performance. Some of the advantages of edge computing are as follows:
Improved Security: Enhanced security as encrypted data is verified as it passes through protected firewalls
Decrease in Cost: In edge computing, data is processed near the source and relevant data is sent to the central network. This saves the cost of computing.
Real-Time Data Access: Helps in accessing temporal data for real-time analytics
Reduces Response Time: One of the major advantages of edge computing is that it reduces response time
As per Forrester, following are use cases generated due to a need for edge computing to conduct complex processing that cloud can’t support, fuelled by the proliferation of connected devices.
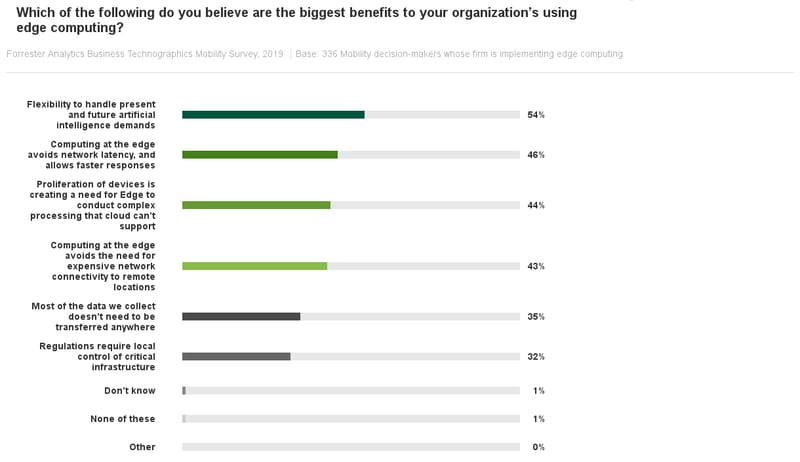
( Image Source : https://go.forrester.com )
Managing a Less Tangible Cloud
Of late, there has been a need to identify where edge is. It needs to be defined what are the main drivers for implementing edge computing, its defining characteristics and the reason for the compute capabilities to be deployed at the edge in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems. But, the other more pressing questions are: “Who owns the edge, who manages the edge, and who uses the edge?”
Well, the simple answer to the question is that we all own the edge. But it comes with the risks for security and privacy coupled with the requirement for standard Application Programming Interface (APIs). On the automation and API front, having a uniform abstraction of where your workload resides, whether it is on edge compute or prem, automation is the key. To have a full-proof security, air-gapped environment both at network and application level should be in place.
Moreover, the devices at the edge needs to have their own keys and be able to authenticate everything including but not limited to securing firmware updates.
Conclusion
Edge Computing is witnessing only the tip of an iceberg. It is more of an ecosystem wherein there is an infrastructure for silicon providers, applications and wider software layers that defines it. Even though it is not a new concept, its adoption is gaining popularity at a rapid pace. As organisations continue to adopt and use IoT technology, the importance of edge computing will grow manifold.