Hey there, soon-to-be Blockchain experts! We’ve simplified the intricacies of Blockchain in this post for our readers. Read on.
Blockchain is like a spreadsheet in the sky, that all participants around the world will have a copy of all transactions. All transactions are recorded in blocks and all blocks together form a strong chain with cryptography and secure hashing. By stringing these words together, the term Blockchain was coined. There are many definitions of Blockchain.
The Blockchain realm also comprises of ‘Bitcoin’. The newbies confuse the two words for each other, however they are disparate but closely related. Bitcoin is a digital currency. Blockchain, on the other hand, is the technology that is used by Bitcoin to allow secure, public and anonymous transactions to take place. For example, think of Blockchain as an operating system (like Windows or Mac OS) and Bitcoin as an application that runs on that operating system.
Blockchain technology is secured with cryptographic techniques, making it near to impossible for hackers to make changes to it. The only way to make changes would be to hack more than half of the nodes in the Blockchain, which means holding more nodes/computers running the blockchain for higher security.
Public Blockchain: A public Blockchain is a decentralized network, which means that no central authority controls the entry of members; and no secret transactions on the network and the consensus mechanism is fully democratic.
Private Blockchain: A member of a Blockchain network writes and verifies each transaction instead of anonymous parties like public Blockchain. This allows for much greater efficiency on transactions by a private Blockchain and it will be completed significantly faster. Of course, it does not offer decentralized security as its public counterpart, but trusting a business to run a Blockchain is no more dangerous than trusting it to run a company without Blockchain.
Member of Blockchain network can also choose who has read access to their Blockchain’s transactions, allowing for greater privacy than a public Blockchain.
Consortium: A consortium Blockchain platform has many of the same advantages of a private Blockchain - efficiency and transaction privacy but consortium Blockchain operates under the leadership of a group of companies instead of a single company.
Do You Need a Blockchain?
This interactive graphic will give you an insight into solving your problem by Blockchain.
Decision Tree:
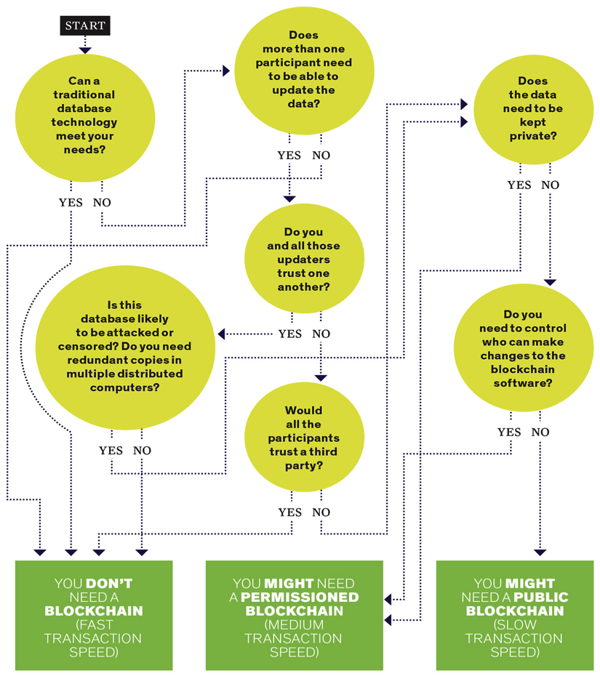
(Image courtesy: https://spectrum.ieee.org)
Blockchain Explained: Supply Chain Use Case
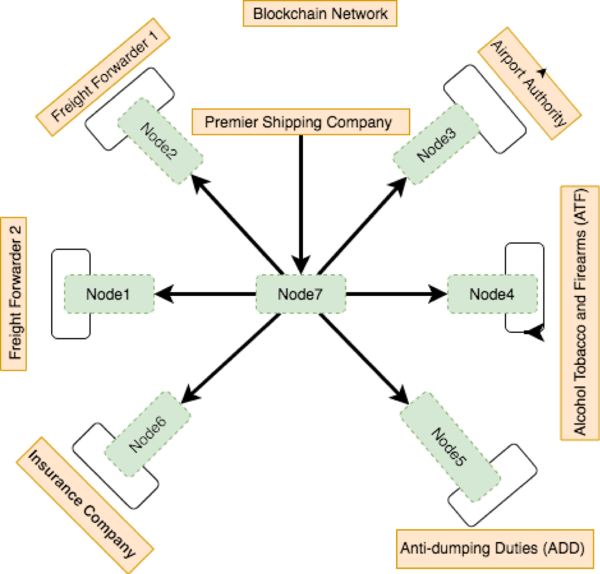
Let us consider a business supply chain network that consists of 7 business entities: Premier Shipping Company, Freight Forwarder 1, Freight Forwarder 2, Airport Authority, Anti-dumping Duties (ADD), Alcohol Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) and Insurance Company.
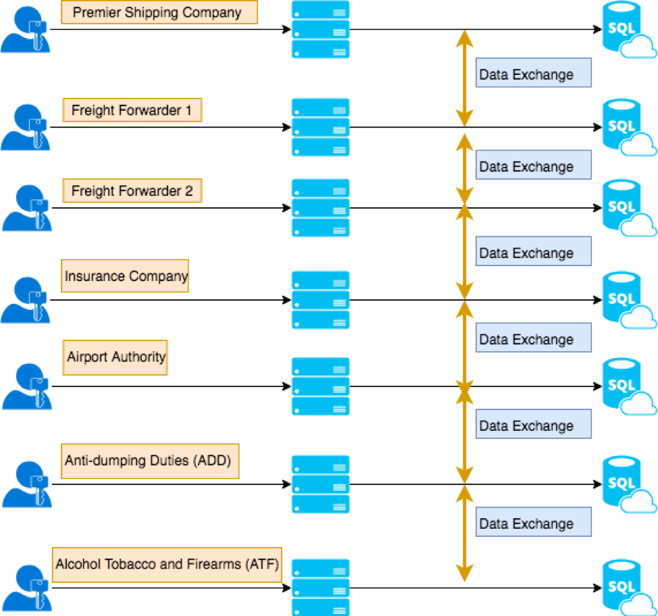
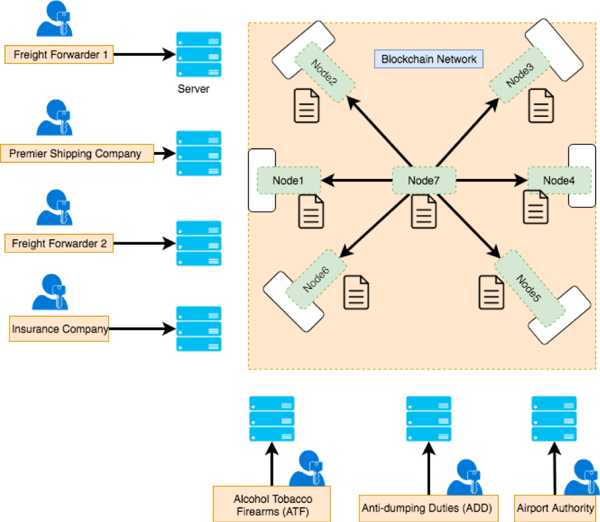
The above image depicts our current software stack. Please see below an elaborated example:
Premier Shipping Company:
A Shipping cargo company has its own software firm to maintain the data of parcels and deliveries. A Shipping cargo company is partnered with freight forwarders to deliver goods effectively to the interior parts of a country.
Premier Shipping Company hold their own web applications to create, update and track the parcels. In a Developer’s terms:
- User Interface: It is a web app, mobile app developed using HTML, CSS, JavaScript (frameworks like React JS, AngularJS, etc.)
- Webserver: Client applications send and receive data from the webserver through rest API calls. This web server is created using Java, PHP, NodeJS and many server-side languages. We do the scaling, clustering of the software here to handle the load of the application.
- Database: The data is stored in any of the databases like MySQL, Postgres, MongoDB etc. The databases are accessed by web server functions with proper authentication. This is the common software architecture at a very high level. FreightForwarder1, FreightForwarder2, Airport Authority, Anti-dumping Duties(ADD), Alcohol Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) and Insurance Company will have the same software firm setup.
Freight Forwarder: A company that receives and ships goods on behalf of other companies. If shipping orders are national (local) orders, there would be no issues as different parties are not involved while shipment moves.
For example, International parcels will be delivered by International shipping company itself and domestic parcels by freight forwarders. This would not involve airport authorities, Anti-dumping Duties (ADD) etc. in entire supply chain life cycle to know about other data.
If there is an order which is sent via international cargo company but will be delivered by freight forwarders; in that case both companies, Airport Authority, Anti-dumping Duties (ADD), Alcohol Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) and customs would be privy to the status of the order, meta data of the order and health status of the order.
Steps in the whole business process:
- Freight forwarders receive parcels from the customer and put the data into their database
- A new entry will be generated in Freight forwarder1, Shipping company, Airport Authority, Anti-dumping Duties (ADD), Alcohol Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) and Insurance company
- It is now dispatched by air after clearance from Airport and other parties and notified to domestic freight forwarders through API’s
- Checking the status of arrival by calling the shipping company APIs
- After getting clearance from arrival port authorities, the cargo will be handed over to domestic freight forwarders
- Once domestic freight forwarder has received, status is updated through APIs
- Everything after that happens through APIs, there is a high possibility that two different status’s may be available in all systems
- Heavy paper work is involved in entire life cycle of supply chain in different formats and there is a high trust factor
- So, overall each entity has its own ledger (copy) that is updated individually with APIs
In 2018, almost all software developers understand full stack web application development - client side development (web apps), web servers (API's), database systems (any database).
If you are a full stack developer or if you know at least one server-side programming language, you can start developing applications on top of Blockchain System.
Why Blockchain?
- If anything happens to goods using smart contracts, claims will be processed easily, since all parties are under the same network
- There is no need to maintain different ledgers as they are updated individually
- Control of the Blockchain lies with the administrators, allowing for access and permissions that are maintained by a central authority
- Since all parties are strangers, Blockchain ensures trust
Now see the Magic of Blockchain- how Blockchain is like traditional software development
Component - 1:
We use client systems to store and retrieve the shipment data. In this example, our client directly makes connection with Blockchain and starts interacting with smart contract functions present in every node of a Blockchain network.
Here is the power of Blockchain, if an entity updates the data in their Blockchain node it will be automatically synced immediately.
You may wonder if all orders would be shared by the parties, however only shared orders need to be synced and shared. It is called privacy of the Blockchain and must be systematically designed. Let us investigate how similar it is for the traditional development.
Component - 2:
Application is developed on top of a Blockchain network, which means each business runs their own Blockchain node and each Blockchain node is interconnected with peer to peer replication mechanism. It is like downloading the clients of Blockchain software from the internet (Ethereum -Geth, Corda, Hyperledger — any one of this) and installing it in their machines. Once two nodes are launched in corresponding systems of respective company with configuration pointing towards each others machines IP addresses. Because the software has default methods to connect with each other. It is just like installing our traditional webserver (ex: tomcat, JBoss, Nodejs).
Component - 3:
In Blockchain system there are no separate databases, data is stored inside the Blockchain node itself and it will be replicated using peer to peer replication concepts such as grpc. You may wonder how to store data inside the Blockchain node, it is just like our web server code (Business logic). This code is called smart contract which is just like other programming languages. If you know anybody skilled in this, it is easy to write smart contracts, sometimes data is stored in the form of smart contracts or we can use decentralized databases such as bigchaindb, IPFS etc.
Component - 4:
Another approach is that rather than clients directly connecting with smart contracts present in the Blockchain nodes, we can introduce the intermediary web server layer, that will interact with the Blockchain network. Refer below an example of the Blockchain structure.
We can create our own architecture based on our needs. Since the eco system is dynamic and evolving, best practices are yet to be defined by the industry. The first two components are traditional and third component is new which is a combination of smart contract and Blockchain nodes.
Database Vs Blockchain:
A database running on the World Wide Web is most often using a client-server network architecture.
A user (client) with permissions associated with their account can change entries that are stored on a centralized server linked to a database, by changing the 'master copy'. Whenever a user accesses a database using their computer, they will get the updated version of the database entry. Control of the database remains with database administrators, allowing for access and permissions to be maintained be a central authority.
This is an entirely different approach with Blockchain.
For a Blockchain database, each participant maintains, calculates and updates new entries into the database. Distributed ledger technology (like Blockchain), users can create database like environments and can maintain multiple mutually untrusting users with exchange value or append records without a central coordinator.
Conclusion:
Blockchains additionally offer atomicity (ability to prevent partial updates to the ledger) to its users, ensuring that all transactions that are fortuitous on each other will be able to execute immediately without allowing for tampering records. I would recommend developers to start with Ethereum, hyperledger fabric for development, which is easy to setup and develop. Once you have completed the first set-up, you will find more similarities in it.
Let’s recollect about what we’ve learned so far in a nutshell:
What is Blockchain?
- A peer-to-peer network that removes the need for trusting third parties
- Transactions are processed quicker and cheaper than standard (non Blockchain) systems
- It is a public database and all transactions are visible on the network, preventing cyber attacks
- The database cannot be changed without more than half of the network agreeing, making it much more secure
- It is not controlled by one single company and it has no single point of failure
- Blockchain can be used in many different industries — not just digital currencies
How will this benefit large industries?
- It removes the cost of third parties from the network
- Payments and data are processed much quicker and easier
- Data replication management between businesses is much easier
- Data protection/security is improved on a large scale